Top-10-Machine-Learning-Algorithms-Beginners-Should-Know-3
Plain Bayes
Plain Bayes is a simple but powerful predictive modeling algorithm.
The model consists of two types of probabilities that can be calculated directly from your training data:
The probability of each category;
Conditional probabilities for each class given each x-value.
Once computed, the probability model can be used to make predictions about new data using Bayes’ Theorem. When the data is real-valued, a Gaussian distribution (bell curve) is usually assumed so that these probabilities can be easily estimated.
Plain Bayes is called plain because it assumes that each input variable is independent. This is a strong assumption that is unrealistic for real data, however, the technique is very effective in dealing with a large number of complex problems.
K-Nearest Neighbor (KNN)
The KNN algorithm is very simple and very effective.The model representation of KNN is the entire training dataset.
Predictions are made for new data points by searching for the K most similar instances (neighbors) in the entire training set and aggregating the output variables of these K instances.
For regression problems, this might be the average output variable, and for classification problems, this might be the mode (or most common) class value.
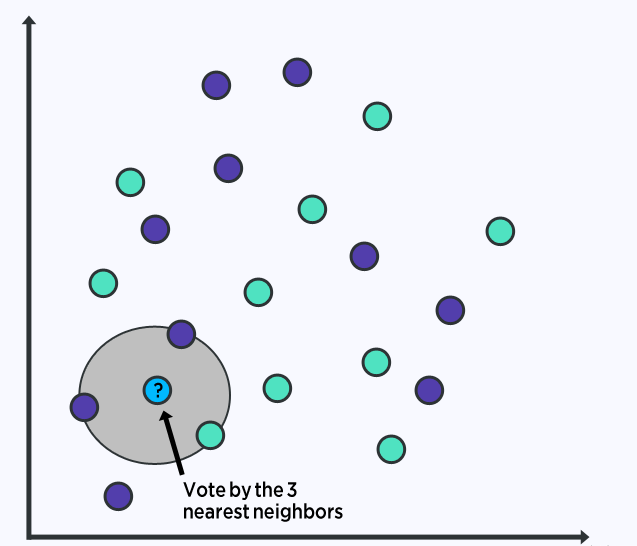
The trick is to determine the similarity between the data instances.
KNNs may require a large amount of memory or space to store all the data, but perform the computation (or learning) in time only when a prediction is needed. This period allows you to update and manage training instances over time to maintain prediction accuracy.