Top-10-Machine-Learning-Algorithms-Beginners-Should-Know-4
Learning Vector Quantization (LVQ)
**One disadvantage of K-Nearest Neighbors is the need to keep the entire training dataset. **
The Learning Vector Quantization algorithm (or LVQ for short) is an artificial neural network algorithm that allows to select the number of training instances to be pegged and to know exactly how these instances look.
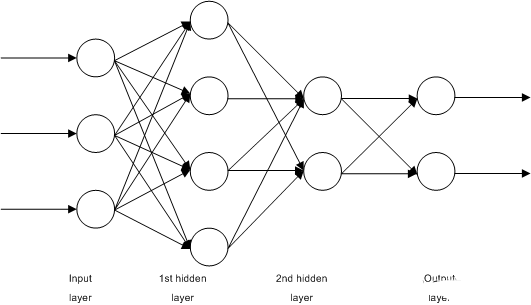
The representation of an LVQ is a collection of codebook vectors. These are chosen randomly at the beginning and are suitable to best summarize the training dataset over multiple iterations of the learning algorithm. After learning, the codebook vectors can be used like K-Nearest Neighbors to make predictions. The most similar neighbors (best matching codebook vectors) are found by calculating the distance between each codebook vector and a new data instance. The class value or (actual value in the case of regression) of the best matching unit is then returned as a prediction.
The best results are obtained if the data is rescaled to have the same range, e.g. between 0 and 1.
If you find that KNN provides good results on your dataset, try using LVQ to reduce the memory requirements for storing the entire training dataset.
Support Vector Machines (SVM)
Support Vector Machines are probably one of the most popular and talked about machine learning algorithms.
Hyperplanes are lines that divide the space of input variables.
In SVM, a hyperplane is chosen to best separate the points in the space of input variables by their class (class 0 or class 1). In two dimensions, you can visualize this as a line, assuming that all of our input points can be completely separated by this line.The SVM learning algorithm finds the coefficients that lead to the best separation of classes by hyperplanes.
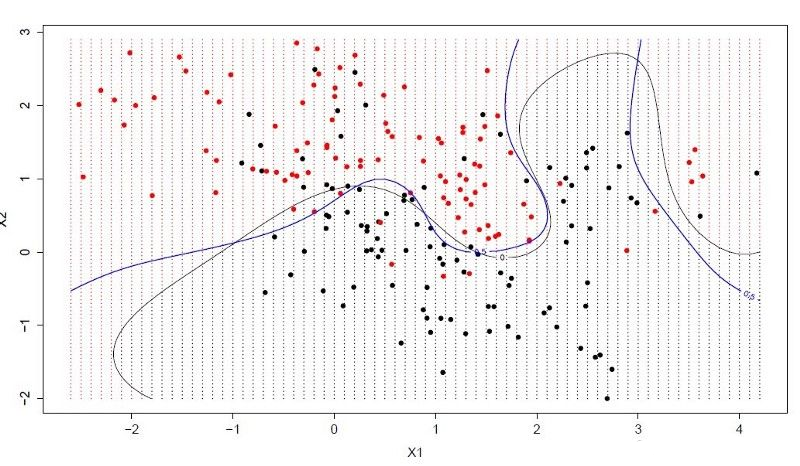
The distance between the **hyperplane and the nearest data point is called the margin.
The best or optimal hyperplane that can separate these two classes is the line with the largest margin. **
Only these points are relevant for defining hyperplanes and constructing classifiers. These points are called support vectors. They support or define the hyperplane. In practice, optimization algorithms are used to find the value of the coefficient that maximizes the margins.