Top-10-Machine-Learning-Algorithms-Beginners-Should-Know-2
Linear Discriminant Analysis
Logistic regression is a classification algorithm traditionally limited to two-category classification problems. If you have more than two categories, the Linear Discriminant Analysis algorithm is the preferred linear classification technique.
The representation of LDA is very simple. It consists of the statistical properties of your data, computed for each class. For a single input variable, this consists of:
- Mean value for each category.
- Variance calculated across all categories.
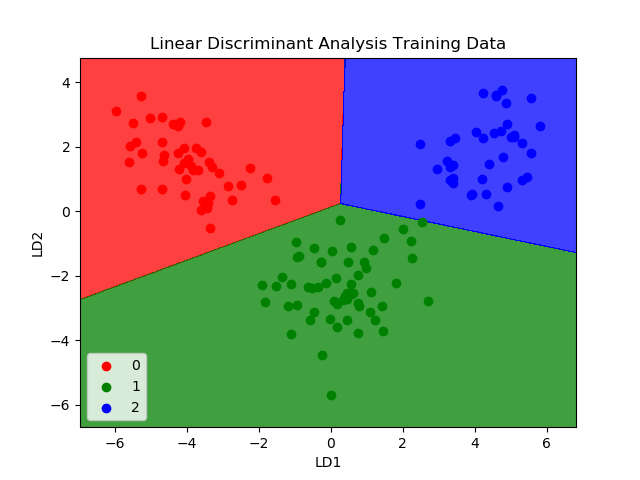
Predictions are made by calculating the discriminant value for each category and targeting the category with the largest value. It is assumed that the data has a Gaussian distribution (bell curve), so it is best to remove outliers from the data beforehand. It is a simple and powerful method for categorical predictive modeling problems.
Classification and regression trees
Decision trees are an important algorithm for predictive modeling machine learning.
The representation of a decision tree model is a binary tree. This is a binary tree from algorithms and data structures, nothing fancy. Each node represents an input variable (x) and a split point on that variable (assuming the variable is numeric).
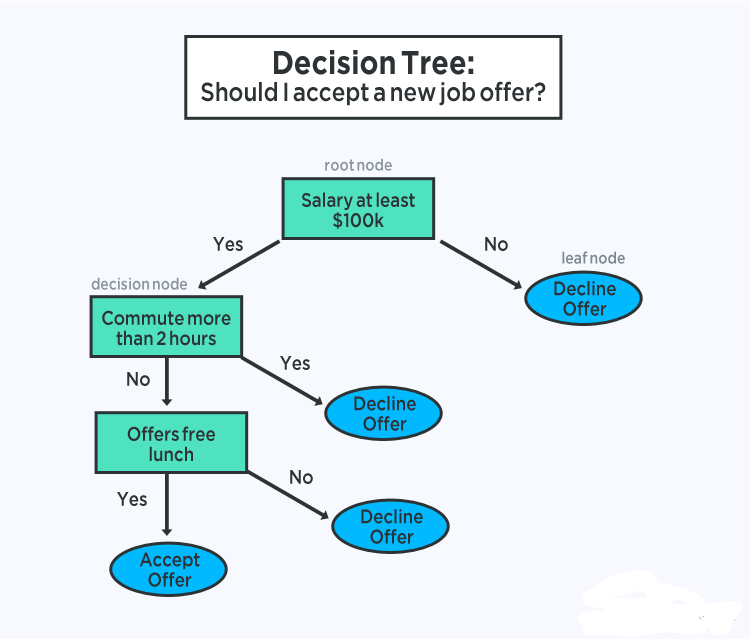
The leaf nodes of the tree contain an output variable (y) that is used to make predictions. Predictions are made by traversing the splits of the tree until a leaf node is reached and outputting the class value at that leaf node.
Trees are also fast at making predictions. They are also usually accurate for a wide range of problems and do not require any special preparation of the data.